Micro DIP Switches Explained
A Micro DIP switch (often called a "half-pitch" DIP switch) is a compact version of the standard Dual Inline Package switch, designed specifically for space-constrained electronic devices. Micro DIP switches function exactly like standard DIP switches—controlling circuit flow via binary ON/OFF positions—but occupy significantly less physical space on the Printed Circuit Board (PCB).
While a standard DIP switch has a pin spacing (pitch) of 2.54mm, a micro DIP switch typically features a 1.27mm pitch, effectively cutting the required board space in half. These components are essential for modern, high-density electronics like handheld devices, remote sensors, and compact industrial controllers where every millimeter of internal real estate counts.
What is a Micro DIP Switch?
A Micro DIP switch is an electromechanical component used to manually configure settings on a circuit board without using software. Just like their larger counterparts, they consist of a row of sliding or rocking actuators packaged in a single housing.
However, the defining feature of the "Micro" variant is its density. By shrinking the spacing between the connecting pins, manufacturers allow engineers to fit more functionality into smaller devices. Because they are so small, they are almost exclusively designed for Surface Mount Technology (SMT), rather than the older through-hole method.
- Learn the basics: To understand the fundamental mechanics behind these components, read our guide on How DIP Switches Work.
The "Half-Pitch" Standard
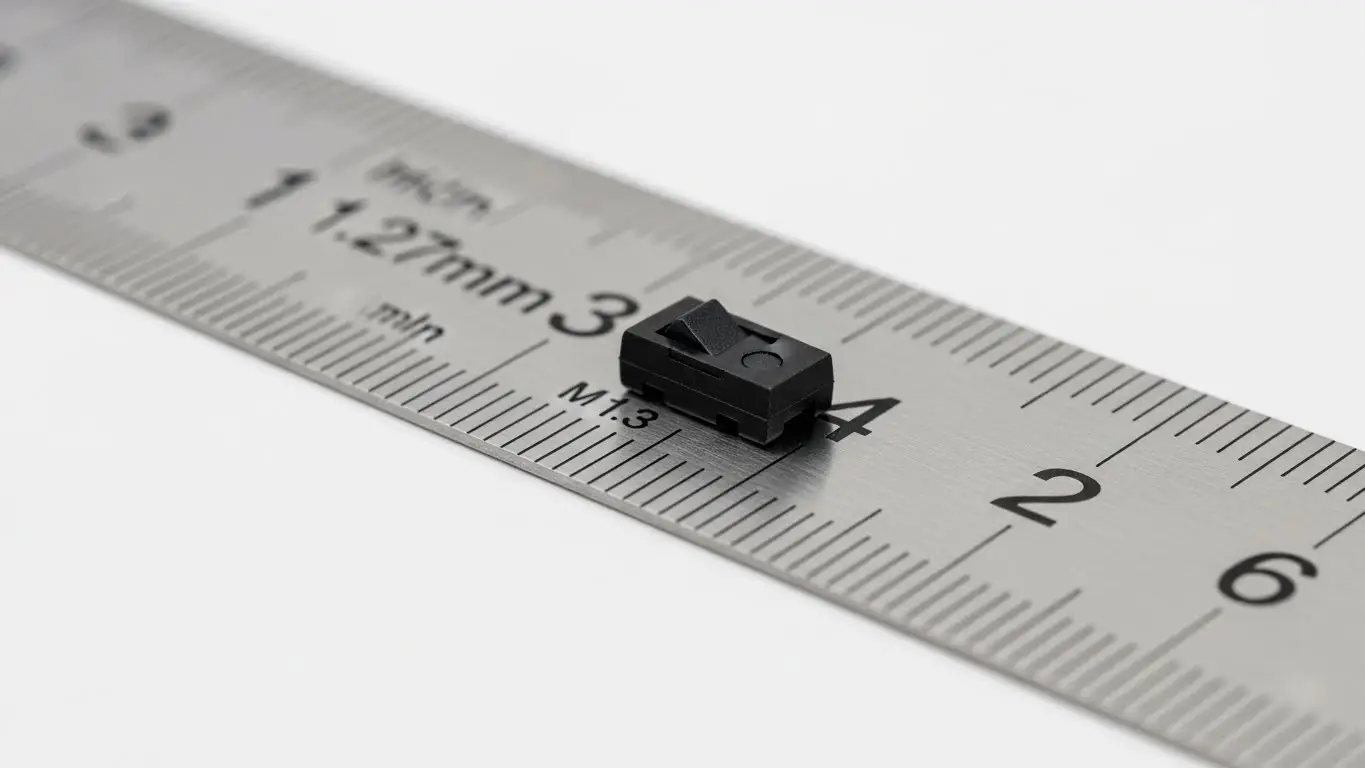
In the industry, you will often hear these referred to as "Half-Pitch" switches.
- Standard Pitch: 2.54mm (0.100 inch) – The classic size.
- Micro (Half) Pitch: 1.27mm (0.050 inch) – The modern compact standard.
Alt Text: Close-up comparison of a black 1.27mm pitch Micro DIP switch next to a ruler showing its tiny scale.
Standard vs. Micro DIP Switches: What’s the Difference?
The primary difference is the terminal pitch and the physical footprint.
While standard switches are large enough to be manipulated by a fingernail or a standard screwdriver, Micro DIP switches require precision tools. Because of their small size, heat management during soldering is also more critical.
Since most Micro DIPs are designed for automated assembly, they fall under the category of SMD components.
- Deep Dive: What is an SMD DIP Switch?
| Feature | Standard DIP Switch | Micro (Half-Pitch) DIP Switch |
| Pin Pitch | 2.54mm (0.1 inch) | 1.27mm (0.05 inch) |
| Actuation | Finger or Screwdriver | Precision Tweezers or Stylus |
| Mounting | Through-hole or SMD | Almost exclusively SMD |
| Current Rating | Higher (typically 100mA) | Lower (typically 25-50mA) |
| Best For | Industrial panels, Desktop PCs | Handhelds, IoT Devices |
What is the Pitch of a Micro DIP Switch?
The standard pitch for a Micro DIP switch is 1.27mm.
Pitch refers to the distance between the center of one pin to the center of the next pin. The 1.27mm spacing is exactly half of the industry-standard 2.54mm spacing used in breadboards and older electronics.
This tight spacing creates "high-density" mounting. It allows designers to place an 8-position switch in the same amount of space that a 4-position standard switch would occupy. However, this precision requires tighter manufacturing tolerances to prevent "bridging" (accidental electrical connections) between pins during soldering.
How Do You Actuate Micro DIP Switches?
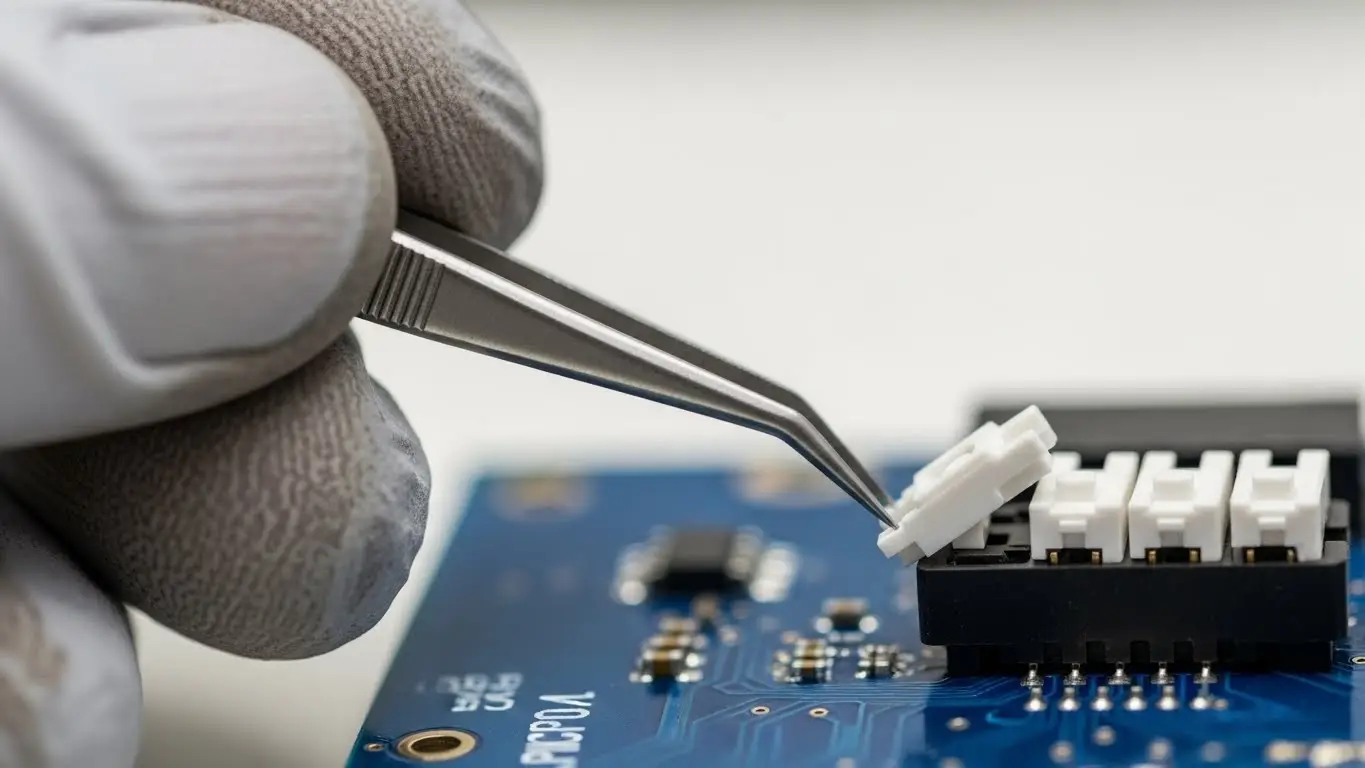
You must use a fine-tipped tool, such as a probe, tweezer tip, or jeweler’s screwdriver.
Because the actuators are incredibly small, using a finger is impossible, and using a standard pencil is dangerous (graphite dust can cause short circuits in such tight spaces).
This brings up an important distinction in switch selection: Usage Frequency.
Micro DIP switches are designed for "Set and Forget" applications. If you need a switch that a user interacts with frequently, a micro DIP is the wrong choice. Instead, you should look for a low-profile tactile switch, which offers a user-friendly interface in a similarly small package.
- Comparison: What is Low Profile Tact Switch
Durability and Environmental Protection
Due to their microscopic internal parts, Micro DIP switches are sensitive to dust and moisture.
Tape Seals
Most Micro DIP switches come with a factory-applied polyimide tape seal on top. This tape serves two purposes:
- Vacuum Pick-up: It creates a flat surface for the robotic nozzle to pick up the switch and place it on the PCB during manufacturing.
- Wash Protection: It prevents flux and cleaning fluids from entering the switch housing during the soldering wash process.
Once the device is assembled, this tape is usually peeled off to allow access to the actuators. If your device needs permanent protection in the field, you must consider the IP rating of the component.
- Related Guide: Waterproof Tactile Switches Explained (Understanding IP ratings for small switches).
Visual Indicators vs. Configuration
Micro DIP switches are strictly for logic configuration. They do not have lights or indicators.
In contrast, consumer electronics often use switches that provide visual feedback to the user, such as an LED lighting up when a button is pressed. While a Micro DIP sets the rules for the device (e.g., "Enable Turbo Mode"), an illuminated switch is what the user presses to activate that mode.
- Learn more: How Illuminated Tact Switch Works
Frequently Asked Questions
It is possible but difficult. Because the pins are only 1.27mm apart, hand soldering requires a very fine soldering iron tip, a steady hand, and magnification to avoid bridging pins. They are designed primarily for reflow ovens.
"Piano" refers to the actuator style (side-actuated rockers that look like piano keys), while "Micro" refers to the size. You can have a Micro Piano DIP switch, meaning it is a half-pitch switch with side-rocker actuators
While standard DIPs are often red or blue, Micro DIP switches are predominantly black. This is because the high-temperature plastics required for the SMD reflow soldering process (like LCP or Nylon 9T) are most stable in black formulations.
They typically have a mechanical life of 1,000 to 2,000 cycles. This is lower than tactile switches because they are intended to be moved rarely.
Key Takeaways
- Definition: Micro DIP switches are half-pitch (1.27mm) configuration switches for compact PCBs.
- Space Saving: They occupy roughly 50% less board space than standard DIP switches.
- Tool Required: Due to their size, they must be adjusted with precision tools, not fingers.
- Mounting: They are almost exclusively Surface Mount (SMD) components.
Conclusion
Micro DIP switches are the unsung heroes of modern, miniaturized electronics. They offer the versatility of hardware configuration without the bulk of traditional components. Whether you are designing a sleek IoT sensor or a compact control module, switching to half-pitch components is a smart move for optimizing board layout.
If you are looking for high-precision switching solutions that save space without sacrificing reliability, explore our catalog.
Browse high-quality micro and standard switches at HX-Switch.