DIP Switches for Communication Devices
DIP switches for communication devices are essential electromechanical components used to manually configure hardware settings like network addresses, baud rates, and termination resistance. Unlike software settings, which can be corrupted or hacked, a DIP (Dual In-line Package) switch offers a physical, non-volatile state that remains constant even during power failures. They are the industry standard for configuring RS-485 networks, IoT gateways, and industrial modems, ensuring that devices communicate correctly on a shared bus. By providing a "hard-coded" setup, they eliminate the need for complex programming tools during field installation.
Why Are DIP Switches Critical for Network Hardware?
In an era of software-defined networking, physical switches might seem outdated, but they provide unmatched reliability and security for communication hardware. When you deploy a remote telemetry unit or a fiber optic transceiver, you need it to wake up with the exact same identity every time.
Physical Security and "Air-Gapped" Configuration
One of the biggest advantages is security. A hacker cannot remotely toggle a physical switch. If a device’s mode is set via a DIP switch, it cannot be inadvertently changed by a buggy firmware update or a malicious script. This "physicality" acts as a hardware firewall for critical settings.
Furthermore, technicians in the field often lack access to laptops or proprietary software. A row of DIP switches allows them to visually verify a device’s configuration (e.g., "Is this unit set to Master or Slave?") instantly without plugging in a diagnostic cable.
How Do You Configure DIP Switches for RS-485 and Modbus?
To configure DIP switches for RS-485/Modbus, you typically use a binary combination to set the unique Node ID and specific switches to enable termination resistance.
In serial communication networks like RS-485, every device needs a unique address. A standard 8-position DIP switch allows for 256 unique addresses (using binary counting from 0 to 255).
- Switches 1-7: Used for the address (Node ID).
- Switch 8: Often reserved to toggle the 120-ohm termination resistor ON or OFF to prevent signal reflection at the end of the cable run.
This contrasts with DIP switches for industrial machines, where switches might control motor speed or voltage levels directly. In communication, they almost exclusively control logic and identity.
What is the Difference Between Rotary and Slide DIP Switches?
Slide DIP switches use individual levers for On/Off states, ideal for binary addressing, while rotary DIP switches use a dial to select a specific digit (0-9 or 0-F).
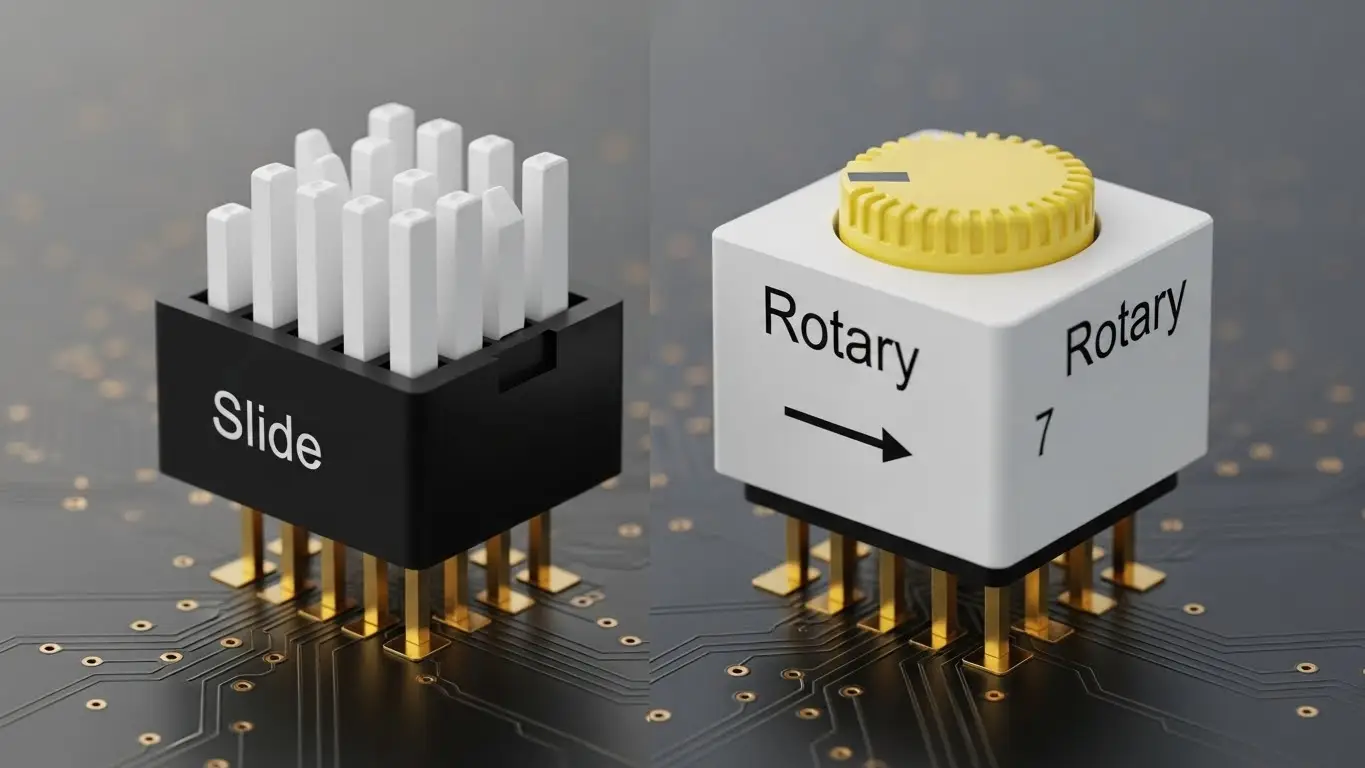
For communication devices, the choice depends on the protocol complexity.
Slide/Piano Style
These are best for "Bit-level" settings.
- Example: Setting Baud Rate. Switch 1 ON might mean 9600 bps, while Switch 1 OFF means 19200 bps.
- Pros: Very visual; easy to see the pattern.
Rotary Style
These are best for "Byte-level" settings or simple ID selection.
- Example: If a technician needs to set a device to ID #5, turning a rotary dial to "5" is much less error-prone than calculating the binary equivalent (00000101) for a slide switch.
For a deeper dive into the mechanical specifications of these variants, check our technical switch application notes.
Comparison: Hardware (DIP) vs. Software Configuration
| Feature | DIP Switch Configuration | Software Configuration |
| Security | High (Physical access required) | Medium (Vulnerable to bugs/hacks) |
| Visibility | Instant (Visual check) | Low (Requires connection tool) |
| Flexibility | Low (Limited positions) | High (Infinite options) |
| Cost | Low (Component cost) | Medium (Development time) |
| Fail-Safe | Excellent (Retains state on power loss) | Good (Dependent on non-volatile memory) |
While tact switches for consumer electronics are designed for constant user interaction, DIP switches in communication hubs are designed to be set once and left alone.
Do DIP Switches Affect Signal Quality?
Yes, poor quality DIP switches can introduce resistance or intermittent connections that degrade low-voltage communication signals.
Communication protocols often run at very low voltages (3.3V or lower) and low currents. If a DIP switch uses tin-plated contacts, oxidation can build up over time, creating an "open" circuit even when the switch is ON.
The Gold Standard
For any communication device (routers, switches, gateways), gold-plated contacts are mandatory. Gold resists corrosion and ensures that the logic signal (0 or 1) is read accurately even after years of inactivity. This is similar to the reliability standards seen in tactile switches for medical equipment, where signal integrity is non-negotiable.
What Are Common Failure Modes in Networking DIP Switches?
The most common failures are contact oxidation due to moisture ingress and mechanical damage from using improper tools for adjustment.
- Flux Contamination: During PCB assembly, if the switch isn't sealed (taped), solder flux can wick inside and insulate the contacts.
- "Half-Switching": If a technician leaves a slide switch in a middle position (neither fully ON nor OFF), the communication controller may read floating signals, causing erratic network behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is generally not recommended. Most communication devices only read the state of the DIP switches during the "Power-On Self-Test" (POST). Changing them while live usually won't take effect until you reboot the device, and in some rare cases, it could cause short circuits.
Many manufacturers ship devices with all DIP switches in the "OFF" position. This usually puts the device into a software-defined mode or a factory default state (e.g., ID #1, 9600 baud).
If a switch is acting intermittently, use a contact cleaner spray specifically designed for electronics. However, if the switch is sealed (IP67), external cleaning won't help internal oxidation—the switch must be replaced.
The numbers (1 through 8, typically) identify the channel. In communication manuals, you will see instructions like "Set SW3 to ON." This refers to the physical switch labeled "3" on the block.
A Piano DIP switch has actuators that stick out to the side rather than up. This is useful for communication devices mounted in rack units, allowing technicians to change settings from the edge of the board without removing the card.
Key Takeaways
- Security & Stability: DIP switches provide a hack-proof, non-volatile method for configuring network hardware.
- Binary addressing: They are the standard method for setting Node IDs and termination in RS-485 and Modbus networks.
- Material Matters: Always specify gold-plated contacts for communication devices to prevent signal loss at low voltages.
- Visual Verification: They allow field engineers to troubleshoot configuration settings without needing a laptop or software interface.
Conclusion
DIP switches for communication devices remain a cornerstone of reliable network architecture. Whether you are designing an IoT gateway or a heavy-duty industrial modem, choosing the right switch ensures your hardware communicates clearly and consistently. By prioritizing gold contacts, proper sealing, and clear labeling, you build a "set-and-forget" reliability that software simply cannot match.