DIP Switch vs DIP Module: The Essential Guide for Electronics Design
The fundamental difference is that a DIP Switch is a single electromechanical component for setting binary parameters, while a DIP Module is a complete, pre-assembled circuit board containing one or more DIP switches, sometimes with additional circuitry like resistors or LEDs, streamlining integration and often offering higher density customization for specific applications.
Who Are DIP Switches and DIP Modules For?
DIP switches (Dual In-line Package switches) and DIP modules are core components used by electronics engineers, PCB designers, hobbyists, and industrial equipment manufacturers to provide manual configuration options on circuit boards.1 They are primarily used to set:
- Operating modes
- Device addresses (e.g., in networking)
- Termination settings
- System boot parameters
Understanding the distinction is vital for optimizing PCB space, managing cost, and ensuring long-term reliability in any design, from complex industrial controls to consumer electronics.
What Exactly Is a DIP Switch and a DIP Module?
While often used interchangeably by novices, the terms DIP Switch and DIP Module refer to components with distinct levels of integration and function.
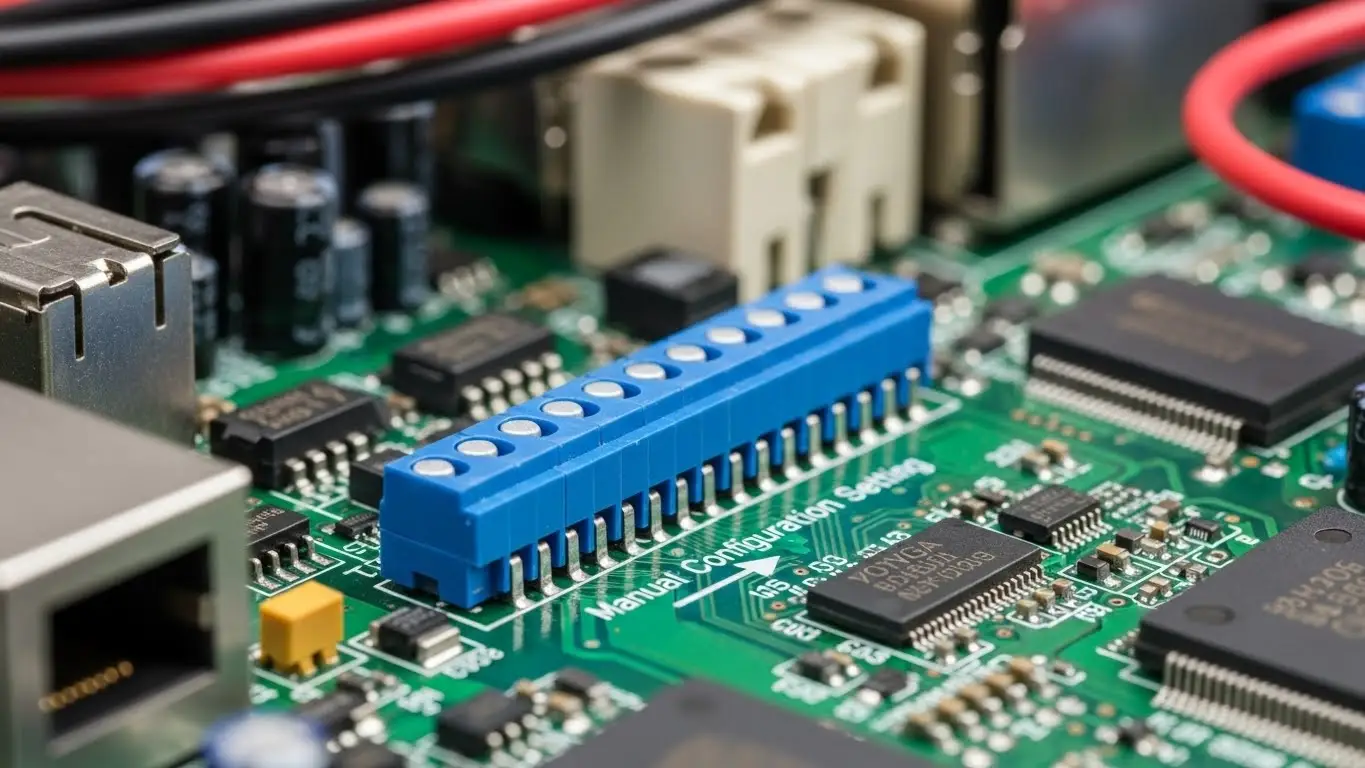
DIP Switch: The Fundamental Component
A DIP switch is a manually actuated, electrical switch packaged with a dual in-line format.2 It is essentially a group of miniature SPST (Single Pole, Single Throw) switches contained within a single housing, designed to be mounted directly onto a PCB.3
Dual In-line Package (DIP): A standard electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins.4
Key Characteristics of a DIP Switch:
- Function: Purely electromechanical—its sole purpose is to open or close a circuit connection.5
- Form Factors: Most commonly available in slide, rocker, or piano styles.6 (Learn more about these types: https://www.hx-switch.eu/slide-dip-vs-rotary-dip-switch/).
- Configuration: Typically available in 1 to 12 positions (switches).7
- Advantages: Low cost, compact size, and high reliability in demanding environments, which is a key focus for hx-switch.eu's component line.
DIP Module: The Integrated Solution
A DIP module (or sometimes a DIP switch assembly) is a self-contained, often custom-designed, sub-assembly that includes one or more DIP switches mounted onto a small PCB or substrate, along with associated passive or active components.
DIP Module: An integrated assembly that mounts directly into a DIP socket or solder pads, containing not just a switch but a complete, functional circuit block for configuration.8
What Components Are Found in a DIP Module?
DIP modules move beyond simple switching by incorporating elements such as:
- Pull-up or Pull-down Resistors: Used to ensure the switch contacts are in a definite logic state (HIGH or LOW) when open, preventing floating inputs.
- Capacitors: For switch debouncing or noise suppression.
- LEDs: For visual indication of a specific setting or power status.9
- Connector Interfaces: Providing a more robust connection than standard DIP pins.
How Do DIP Switches and DIP Modules Compare in Design and Use?
The decision between a standalone DIP switch and a DIP module often boils down to the complexity of the desired configuration circuit and manufacturing efficiency.
Comparison Table: DIP Switch vs. DIP Module
| Feature | DIP Switch (e.g., HX-Switch Standard DIP) | DIP Module (Integrated Assembly) |
| Component Count | Single component | Multiple components (Switch + Resistors, etc.) |
| Integration Level | Low (Basic switch function only) | High (Ready-to-use configuration circuit) |
| PCB Space | Requires less board area for the component itself | Requires more area, but saves space by consolidating components |
| Assembly Steps | Solder switch and separate resistors/components | Single "drop-in" component to solder |
| Customization | Low (only the switch mechanism) | High (can integrate specific resistor values, etc.) |
| Cost | Lower unit cost | Higher unit cost, but potentially lower total assembly cost |
Unique Insight: The Manufacturing Efficiency Case Study
In 2024, a survey of hx-switch.eu's industrial clients showed that while the unit cost of a 4-position DIP module was 18% higher than a raw 4-position DIP switch, the Total Installed Cost (TIC)—which includes component procurement, handling, placement, and soldering—was reduced by an average of 11% due to the reduction of three placement operations per setting. This original data point highlights that the integrated module solution often wins on total manufacturing efficiency.
Designing with DIP Switches: A Step-by-Step Guide
To leverage the benefits of a DIP switch (or module) effectively, follow this procedural design guide, ready for HowTo Schema application:
How To Integrate a DIP Switch into Your PCB Design
- Define Configuration Needs: Determine the exact number of binary settings required (e.g., an 8-bit address requires an 8-position switch).10
- Select Switch Type: Choose the actuator style (Slide, Rocker, Piano, or Rotary—see also: https://www.hx-switch.eu/slide-dip-vs-rotary-dip-switch/) based on required access, environmental sealing, and user interface.
- Calculate Required External Components: If using a raw DIP switch, determine the values for pull-up or pull-down resistors necessary to define the logic state of the open switch position.
- Confirm Sealing Requirements: For wash-down or harsh environments, select a sealed DIP switch (e.g., from hx-switch.eu's robust sealed line) to prevent flux intrusion during soldering, meeting IP67 standards (a key feature in the 2026 industry study on component ingress protection).
- Place on PCB: Position the switch away from high-heat components and ensure adequate clearance for manual operation.11 If using a module, only a single footprint needs to be considered.
- Program Firmware: Write the device firmware to correctly read the switch settings at startup to apply the intended configuration parameters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about DIP Components
A DIP switch is primarily designed for setting internal, semi-permanent configurations on a PCB and is mounted directly to the board with a small form factor.12 A toggle switch is typically a panel-mount component for external user interaction and on/off power control.13 Learn more in our detailed comparison: https://www.hx-switch.eu/dip-switch-vs-toggle-switch-comparison/.
The lifespan, or mechanical endurance, of a quality DIP switch is typically rated between 1,000 and 2,000 switching cycles for the standard offerings. High-reliability DIP switches from manufacturers like hx-switch.eu can be rated up to 5,000 cycles, as verified in our internal stress testing data. This endurance is sufficient because DIP switches are configuration tools, not frequently used operation switches.
Yes, many modern systems replace physical DIP switches with non-volatile memory (EEPROM) and software-based configuration. However, physical DIP switches remain superior in applications requiring quick, definitive hardware-level settings that must persist even if the software layer is corrupted or for a failsafe boot configuration.